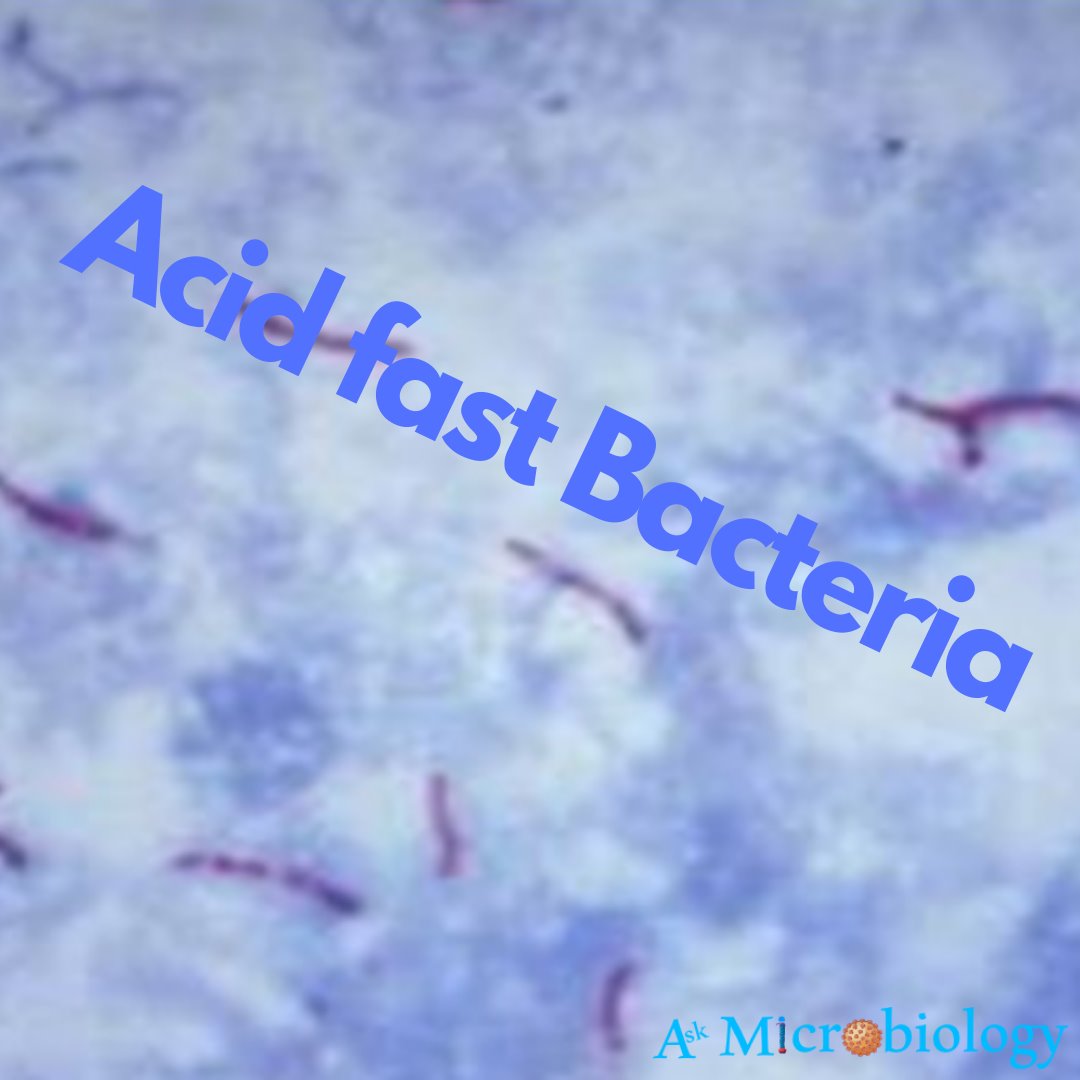
Acid-fast bacteria are those bacteria that have mycolic acid in their cell wall. These bacteria stain acid-fast positive. This bacterium was first discovered by Ziehl–Neelsen that’s why the staining is also named by the scientist i.e Ziehl–Neelsen staining.
Examples:
So in our article, we’ll consider this as a reference to define Acid Fast Bacteria.
Properties of acid-fast bacteria:
These bacteria are strict aerobes, acid-fast positive, rod-shaped bacilli. Their cell wall is composed of a very thick layer of wax and lipid called mycolic acid. It is a very slow growing bacterium. It takes 14-21 days to form a colony. These bacteria did not uptake gram stain. They remain colourless when these bacteria are stain with gram stain.
Why these bacteria are acid fast:
These bacteria have a thick mycolic acid layer around their cell wall. Mycolic acid is a thick lipid membrane. The mycolic acid doesn’t allow gram stain to penetrate and stain the cell wall.
The procedure of acid-fast staining:
First, bacteria are stained with Carbol fuchsin. Primary dye penetrates in the mycolic acid. Carbol fuchsin gives bacteria pink colour. When acid alcohol is added, the extra stain is washed out. Only acid-fast bacteria remain coloured. When secondary dye methylene blue is added, non-acid fast bacteria uptake the secondary dye. Then, this is observed under 100X microscope.
Habitat:
It is present in soil and air.
Diseases caused by acid-fast bacteria:
Acid-fast bacteria cause tuberculosis in humans and also in the animal. It is a zoonotic disease. It causes severe illness in poor people. It produces disease of the respiratory tract as it is an aerobic bacterium. Pathogenicity of this bacterium includes the presence of thick lipid layer around the cell wall that suppresses the immune system of the host. It is a slow-growing bacterium so the immune system didn’t recognize the division of bacteria. It forms the caseinous tubercle in the lungs. These tubercles burst and release bacteria in surroundings. This tubercle may travel from one place to another and produce tuberculosis of the bone.
Diagnosis:
They are fastidious bacteria. These bacteria can’t grow on simple media. For the culturing, LJ media is present to grow.
But rapid diagnostic tools are also present to diagnose this disease. Chest X-ray is used to detect the presence of tubercle formation in the lungs. PCR can be used to diagnose this disease.
Treatment:
There is an issue to treat disease caused by this bacterium. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is now a pan-drug resistant bacterium. There is no line of defence to treat this disease.

An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a coworker who had been doing a little research on this.
And he actually ordered me lunch simply because I stumbled upon it for him…
lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!!
But yeah, thanks for spending the time to discuss this matter here on your web page.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Just wish to say your article is as surprising. The clearness in your post is simply cool and i could assume you’re an expert on this subject. Well with your permission allow me to grab your feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please carry on the gratifying work.
Woah! I’m really enjoying the template/theme of this site. It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s difficult to get that “perfect balance” between superb usability and visual appeal. I must say that you’ve done a amazing job with this. Additionally, the blog loads extremely quick for me on Safari. Outstanding Blog!
It’s impressive that you are getting ideas from this piece of writing as well as from our dialogue made here.
My developer is trying to persuade me to move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using WordPress on a variety of websites for about a year and am worried about switching to another platform. I have heard good things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can transfer all my wordpress posts into it? Any kind of help would be really appreciated!
Fascinating blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a few simple adjustements would really make my blog stand out. Please let me know where you got your design. Thanks a lot
Everything is very open with a clear explanation of the challenges. It was definitely informative. Your site is extremely helpful. Thanks for sharing!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
What’s Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It positively helpful and it has helped me out loads. I’m hoping to contribute & assist other users like its helped me. Good job.
Good insights here. Design definitely affects how long users stay
on adult platforms
Also visit my blog post; gay porn
Solid perspective. Modern adult platforms feel very distinct from older ones
My webpage: https://gay0day.com/videos/108772/georgia-inmate-getting-screwed-by-prison-dad/
Good points. Navigation really matters on adult video websites
Feel free to surf to my blog https://thetranny.com/videos/51464/ladymans-riding-weenies-compilation-reverse-cowgirl/
Good blog you have got here.. It’s hard to find good quality
writing like yours nowadays. I really appreciate individuals like you!
Take care!!
I visited various websites but the audio quality for audio songs
existing at this site is really marvelous.