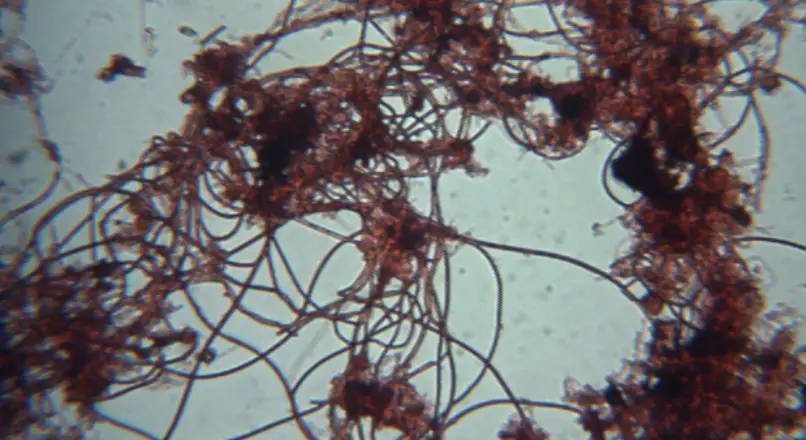
Filamentous Bacteria
Filamentous bacteria are those bacteria that produce long mesh-like filament by growing end to end. These bacteria are seen as long strands under the microscope.
These bacteria are present in sludge areas for better settling. They are also present in water treatment areas.
- These bacteria have long thread-like structures such as clumps and chains.
- They provide a backbone for other filament bacteria to attach to the surface.
- They can produce foam upon aeration in a water treatment plant.
Characteristics of filamentous bacteria:
These are some of the characteristics of Filamentous bacteria, These characters help in identification of filamentous bacteria.
Filament shape:
They are present in the form of
- Straight chains
- Smoothly curved
- Irregular Shapes
Filament size
It may range in size from 0.8-5 µm in width and from 5->500µm in length.
Bacterial cell shape:
They may appear as
- Bacillus shape
- Square
- Rectangular
- Barrel-shaped cell
Presence of septa:
Some filamentous bacteria have septa. Septa are the membranes that are present between the two cells. These septa are clearly visible under the microscope. But some filamentous bacteria don’t have the separation between the bacteria.
Sheath:
Some filaments have cells that are stacked together. The cells are firmly attached with the sheath. Some filaments don’t contain sheath. These sheaths vary in size and shapes.
Attached growth:
Attached growth is also called an epiphyte. It grows perpendicularly along a filament. This structure is optional for filamentous bacteria.
Branching:
Branching is the main characteristics of filamentous bacteria. It may either true or false branch. True branching is the presence of continuum between the branches. Some bacteria just appear the formation of branches where two filaments join together.
Identification of filamentous bacteria:
The bacteria can be identified by using staining. There are many stains such as gram stain and Neisser stain that are used to identify filamentous bacteria.
Gram’s staining:
Gram’s staining differentiates the bacteria into two categories as gram positive and gram negative. Gram-positive bacteria are purple in colour because it retains crystal violet dye. Gram-negative bacteria retain safranin dye colour and are pink in colour.
E.g. Nocardia sp. gives crystal violet colour on staining.
Most of the filamentous bacteria are gram-negative only few are gram-positive.
Neisser stain:
It distinguishes the bacteria into two groups. Some bacteria store polyphosphate in the form of granules. Neisser positive stains give a bluish purple colour that indicates the accumulation of polyphosphate. Neisser negative stains give brown colour.
Many filamentous bacteria are Neisser positive and few are Neisser negative.
